
The data obtained were processed in the own software so we set the appropriate regression functions describing the thermal behaviour of radiating panel, which was then used for long-term thermal performance simulations in software TRNSYS. Then we carried out seven simulations of chosen radiating panel with these boundary conditions by means of computational fluid dynamics method (CFD) in the software Fluent. Next we assumed a variable mean temperature of water flowing through the radiating panel in order to be able of computing its thermal performance. From this file of data, we selected seven typical combinations of equivalent sky temperatures, external air temperatures and wind velocities in order to cover the external conditions during the summer nights. The radiating panel is used to cool down the cooling water by convection and heat radiation against the night sky.Īt first we processed the real hourly climatic data for city Brno and by using the extra-terrestrial solar irradiation we calculated night sky temperature during cloudy conditions and other necessary climate parameters for the long-term simulations.

We have considered a cooling system consists of radiating panels placed on the roof, connected by pipes with the cooling ceiling in an office room.
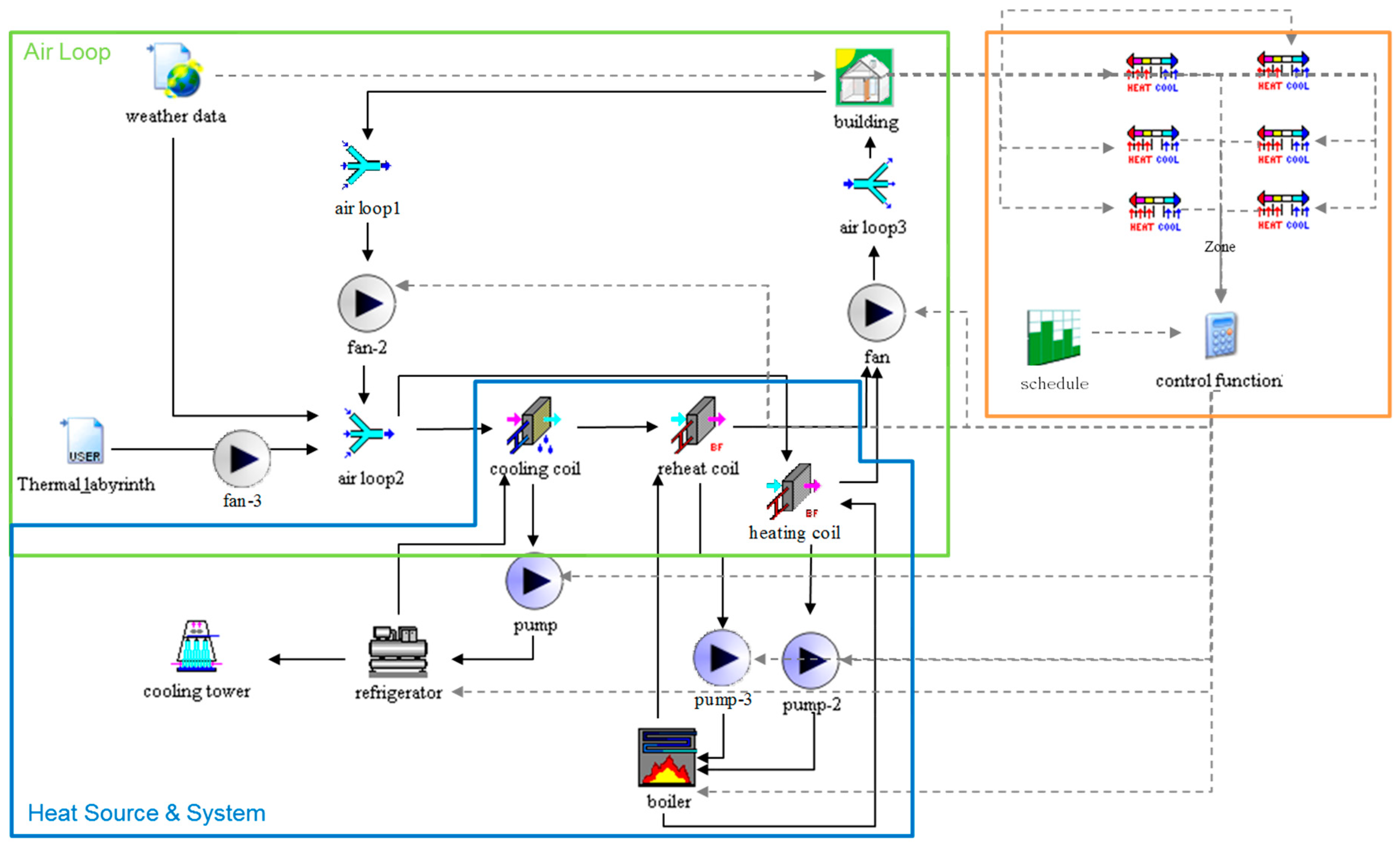
The numerical simulations of non-steady heat transfer and internal thermal comfort evaluation in an office room has been performed. The paper deals with theoretical efficiency evaluation of night sky cooling in climatic condition of Czech Republic. One of possible methods, mainly in desert areas, is using thermal radiation against night sky. Redundant heat removal in summer can be realized in various ways. Energy necessary for cooling of building in summer season makes a big part of energy required for building operation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
